.jpeg)
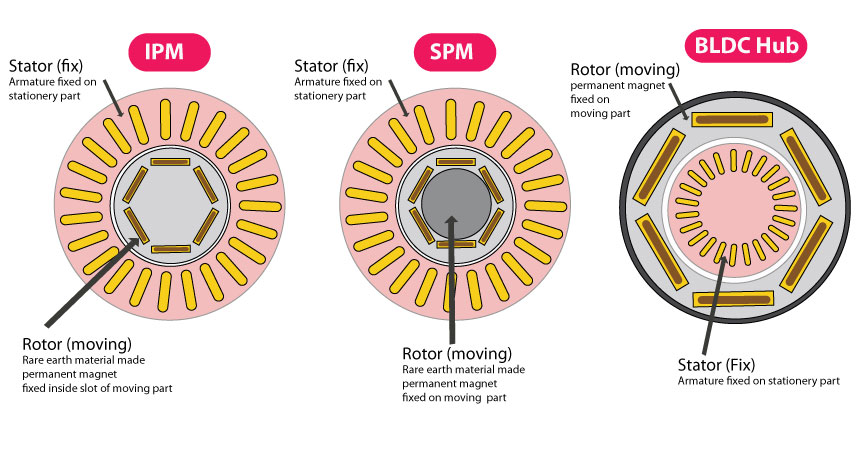
Interior Permanent Magnet (IPM ) is an AC supply motor in which rare Earth material-made super magnet install inside the slot of the Rotor and coil winding (Armature) is fixed on Stator. compare to other IPM motors has high efficiency, high reliability, high torque, and great power density.
Surface permanent magnet (SPM) is also an AC current supply motor configuration in which a super magnet is installed on the surface of the Roter. SPM motors also delivered high torque, high efficiency, and high reliability.
like IPM motor SPM is also a synchronous motor but here permanent motor has been mounted on the surface of the rotor and the armature is fixed on the stator. in SPM reluctance torque is minimum so torque generated in it is less than IPM motor.
Note: SPM and IPM both are a type of PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor).
Brushless Direct Current Moter (BLDC) is DC current-driven motor in which armature winding is fixed on the stator and a permanent magnet is fixed on the outrunner rotor.
Reluctance Torque: the meaning of reluctance is a tendency to oppose, the mounting of a permanent magnet inside the slot of the rotor minimizes the reluctance (oppose of magnetic field ) of the armature magnetic field due to this a torque is generated which is called reluctance torque.
so this is an overview of IPM, SPM, and BLDC motors before going into details let's know about electric motors and their terminology so that we understand each motor configuration performance.
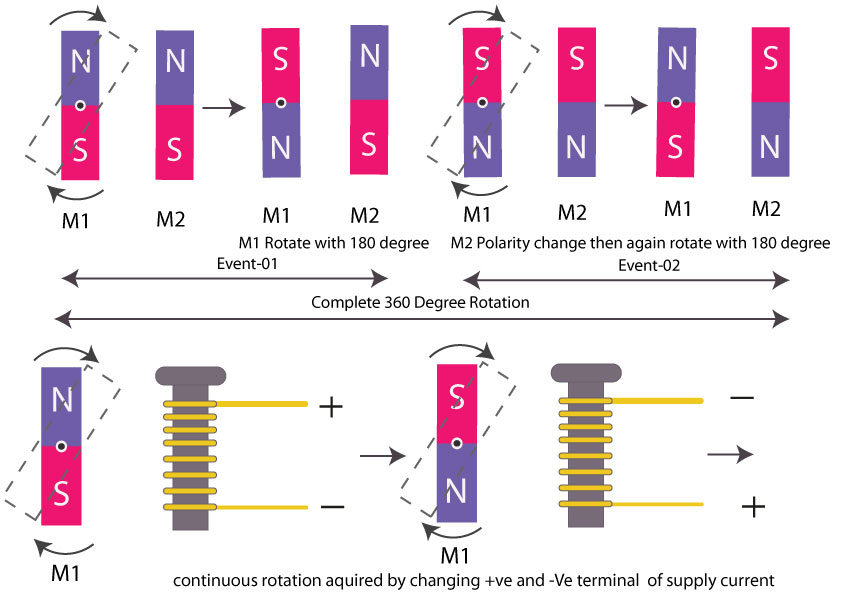
start from zero when two permanent magnets M1 and M2 where magnet M1 can rotate on its axis and M2 bring close together then different poles of each magnet attract each other and similar pole will be repelled in such case fixed magnet will move with 180 degrees if anyhow we change the polarity of magnet M2 again Magnet completes its one rotation ie 360 degrees
for rotation continue we have to change the polarity of the second magnet for every half rotation of magnet M1 which is physically not possible with a permanent magnet but if magnet M2 can be replaced with another magnet whose polarity and its magnitude of the magnetic field can control, then magnet M1 will continue in rotation.
To solve this problem copper winding on an iron core which is known as the armature is introduced which generates an electromagnetic field when current passes through it. so here we have our desired magnet whose electromagnetic field exists due to current, so any change in the current electromagnetic field also will be changed
as an example, if the current direction -ve and +ve terminal of the connection interchange then the polarity (north and South pole ) will be interchanged, and similarly if the current intensity changes then the electromagnetic field strength also will be changed.
A basic Electric having the following parts ---
Roter: it is the moving part of the motor in the basic electric motor armature that works as a rotor.
Stator: it is a fixed part of a motor. in a basic electric motor permanent magnet is fixed on the stator.
Accumulator: it is two half or four-quartered copper-made circular rings connected with carbon brushes. the accumulator is fixed on the motor shaft. the accumulator is responsible for changing the direction of the current supply in coil winding.
Shaft: The armature is fixed on the iron rod which rotates when the motor is on. motor shaft transfers power to the machine
The performance of the motor is measured from five quantities. this very important part of our discussion. it helps us to understand the performance of the motor in electric vehicles when we see the vehicle specification sheet.
Efficiency: it is the ratio of power delivered by the motor and input power of supplied current.
Horsepower(HP): it is the measurement of power required to move a body from one point to another in a given time.
suppose two motors M1 and M2 have different power 5HP and 10HP respectively it means for the same load Moter M2 willl move more fast then M1 or for the same speed M2 carry More load than M1
Brake Horsepower (BHP) & Horsepower (HP): in the EVs specification sheet sometime we see power given in BHP, which means power delivered from the wheel of Evs while HP is Power delivered by the rotor of the motor
Torque: it is the rotatory motion force required for moving an object on its axis it is measured in Newton meters (N-m)
Tarque= Force X Radius ( distance between shaft axis and the surface of the rotor)
in the motor due to electromagnetic force applied on rotor torque is generated.
if torque is high then we can say the motor load carrying capacity is high without changing speed.
RPM: it is a short form of revolution per minute as named it is the total rotation of the rotor in one minute. RPM is directly related to the speed of Evs if the RPM of the motor is high then
Power density ratio: it is the ratio of power delivered by the motor and volume occupied by the motor
if power density is high means a small size of the motor will deliver more power than others
when current is supplied in the armature electromagnetic field is generated and this electromagnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of a permanent magnet and creates a moving force that is called torque this torque rotates the rotor, and RPM has come in existence this RPM has the ability to move the wheel of vehicles so we can say power delivered.
so we can clearly see Torque, RPM, and Horsepower are interrelated so after the mathematical calculations scientists introduce a universal expression
HP= T x RPM / 5252
above expression give some observation
The answer is both, depending on the work type assigned to the motor if we want to move Evs fast then Horsepower is important while if want our Evs to lift Heavy-weight or start quickly ie high pickup then Tarque is more important. in the common word, we can say High torque Evs are more powerful.
The EV industry needs a powerful motor that has a low size, low cost, high range, high power density, and high reliability. To achieve this goal engineers are continuously developing different types of motors. among these three types of motors are very popular in the EV industry. these are interior permanent motors (IPM), surface permanent magnets (SPM), and Brushless direct current motor hub motors (BLDC).
as earlier we have discussed that the IPM motor has better performance than the BLDC hub motor so the IPM motor currently dominates the EVs market because compared to BLDC it occupied less space and performs high torque and high range. the only problem with IPM is its Cost due to the inverter and electronics control system required IPM EVs cost 20% more costly than BLDC hub motors
BLDC hub motor is also popular in the EVs market. many premium Evs bikes have a BLDC hub motor as an example in India top 5 best-selling EVs scooters are OLA S1, TVS iQube, Ather 450X, bajaj chetak, and Okinawa Praise Pro. OLA S and Ather 450X are using IPM and PMSM motors while TVS iQube, bajaj chetak, and Okinawa Praise Pro have come with BLDC Hub motors.
low and high is declared only with respect of these three kinds of motor
| Specification | IPM | SPM | BLDC Hub Motor |
| Current input type | AC | AC | DC |
| Inverter Required | Yes | Yes | No |
| Rotor (moving part) | Permanent Magnet (inner part) | Permanent Magnet (inner part) | Permanent Magnet (Outer part) |
| Stator (fixed part) | Armature (outer) | Armature (outer) | Armature (inner) |
| Control | Complex | Complex | easy |
| Efficiency | High (90 to 95 %) | High < IPM | Moderate (85 %) |
| Horsepower | High | High | Low |
| Torque | High | High | Low |
| Range | High | High | Low |
| Power density ratio | High | High | Low |
| Load Capacity | High | High | Low |
| Reliability | High | High | Low |
| Cost | High | High | Low |
if the cost does not matter and you want a powerful motor that has a high range and high pickup, and high load capacity then go with the IPM motor
but if cost is a matter and ok with slightly less performance of motor then go with BLDC motor
be careful here with battery cell capacity and overall build quality, driving comfort ness also required to see before purchase.
All Comment (1)
Well described